Choosing unmanaged VPS hosting gives you control over server configuration and costs but also places responsibility for setup, security, and maintenance on you. This practical checklist covers eight high-level criteria to evaluate providers so you can match specs to workload, avoid surprises, and reduce risk. It includes performance and storage specifics, network bandwidth considerations, tooling, support, and reputation. I also mention providers to compare — including SpeedyPage.com, which I use and find consistently fast and reliable.
Table of Contents
What is Unmanaged VPS Hosting?
What is unmanaged VPS hosting is a question about who manages the server environment and the level of hands on responsibility you accept when you choose a VPS without managed services. VPS hosting without management gives you full root access, so you control the operating system, security patches, software stacks, and backups, while the provider supplies the underlying compute, storage, and network resources.
Before you choose an unmanaged hosting plan, confirm you have the skills or support to handle setup, monitoring, updates, and restores. If you’re still weighing whether unmanaged hosting is the right fit, see Managed vs Unmanaged VPS: When DIY hosting makes sense before you commit.
Also, verify the provider documents some of these important specs: CPU and memory allocations, storage type and IOPS, and network bandwidth with its speed.
Backup options are typically only available via a web control panel. However, some hosts don’t provide a panel and the cost will be less. Also, some hosts will offer a panel for an added fee or at a higher cost plan.
Optionally, for advanced skills, see if there are any available snapshots or APIs to automate routine tasks. I personally don’t use these aspects.
1. Compute performance: CPU and memory guarantees
- Why it matters: CPU type, clock speed, and dedicated vs shared vCPU affect processing under load; RAM determines how many concurrent processes you can run.
- How to evaluate: Look for guaranteed or dedicated vCPUs, clear CPU clock info if available, and explicit RAM allocation. Avoid vague “shared” allocations with no baseline or values listed.
- Quick check: Match CPU/RAM to your app’s profile (e.g., PHP/WordPress needs moderate CPU but benefits from more RAM).
2. Storage performance and capacity (NVMe/SSD, IOPS)

- Why it matters: Storage type and performance (throughput and IOPS) often have the biggest impact on real-world responsiveness.
- How to evaluate: Prefer NVMe drives (or at least SSD) for proper workloads; check listed disk size along with IOPS or throughput figures. Note whether storage is local (faster) or network-attached; however, most won’t say.
- Quick check: For WordPress and small apps, NVMe + 40–100 GB with adequate IOPS is a solid starting point; larger databases need both more capacity and higher IOPS.
- VPS Hosts Search
- https://www.vpsbenchmarks.com/hosters
- https://www.vpsserver.com/en-us/
- https://speedypage.com/vps (select a location in U.S. or other country, and see listed plans)
3. Network bandwidth and throughput (capacity and link speed)
- Why it matters: Bandwidth allocation and network interface speed determine data transfer limits and latency under load.
- How to evaluate: Look at included transfer allowance (e.g., 12 TB/mo) and the physical link speed (e.g., @10 Gbps NIC). Check whether overage rates are reasonable and whether burst behavior is documented. Most offer @1 Gbps external network speed and offer higher link speeds for a fee or only given with higher plans.
- Quick check: For media-heavy sites or high-traffic APIs, prioritize higher monthly transfer allowances plus a higher NIC speed (1–10 Gbps).
4. Uptime, reliability, and SLA
- Why it matters: Consistent availability prevents lost users and reduces emergency maintenance.
- How to evaluate: Review published uptime percentages, SLAs, historical status pages, and third-party monitoring if available. Smaller hosts may not post formal SLAs but still deliver strong uptime—verify via trials.
- Quick check: Target providers with historical uptime at or above 99.9% for production services.
5. Security features and backup & restore options
- Why it matters: Unmanaged means you handle OS-level security, but some providers offer some basic protections. Many don’t include backups. So, for the server, use your own web control panel, e.g., DirectAdmin for that. For just website backups, use your own backups plugin, e.g., WPvivid.
- How to evaluate: Verify snapshot and backup offerings, retention windows, encrypted storage options, firewall/DDoS protections, and private networking. Even if not provided by host, a good web control panel, like DirectAdmin, will install and manage the CFS firewall with initial basic protections enabled.
- Quick check: Ensure you setup your own automated backups, using your web control panel such as DirectAdmin or cPanel. Understand server restore procedures and test them where possible, before adding websites. Especially test the server restoration before getting too far along on configuring the server.
6. Control panel, API, and management tooling

- Why it matters: Good tooling speeds routine operations even if the plan is not managed.
- How to evaluate: Look for SSH/root access, web console, image templates, snapshot management, and a REST API for automation. Confirm ease of resizing instance types and attaching storage, if that’s what you desire.
- Overall, consider having your own web control panel, such as DirectAdmin or cPanel.
- Quick check: If you use CI/CD or automation, prioritize providers with a mature API and clear docs.
7. Support resources and documentation

- Why it matters: Clear documentation and responsive support reduce time spent troubleshooting.
- How to evaluate: Review knowledge bases, setup guides, community forums, and support channels (ticket, chat). Note whether paid managed options exist for occasional help.
- Quick check: Send a pre-sales question to gauge responsiveness before committing. However, the real test is for technical support. So, consider a small server plan for 1 month’s fee to test support ticket responsiveness.
8. Pricing model, billing predictability, and provider reputation
- Why it matters: Predictable costs and a trustworthy provider make long-term planning smoother.
- How to evaluate: Compare hourly vs monthly billing, bandwidth overage policies, backup/snapshot costs, and fees for routine operations. Research reputation via forums, benchmarks, e.g., VPS Benchmarks, and customer reviews. Consider niche hosts when they offer specialized strengths.
- Quick check: Build a sample monthly cost for expected usage including backups and transfer; prefer transparent fee lists.
Quick checklist
- Well-stated vCPU, CPU speed + clear RAM allocation details (type, version, size)
- NVMe/SSD storage or stated IOPS throughput
- Some providers will also display their NVMe version for faster speeds, e.g., v4 and higher
- Monthly transfer allowance + NIC speed (e.g., 12 TB @ 10 Gbps)
- Most providers default to basic network speed @ 1 Gbps; higher speeds are strongly desired.
- Published uptime history or SLA (target 99.9%+ for production)
- Some might offer backups/snapshots with documented restore steps
- SSH/root access
- Up-to-date docs and reasonable support response
- Most unmanaged server plans don’t require very many docs due to the provision of automated O/S installations. After that, it’s up to you and your selected web control panel, which has its own branded guides.
- Transparent billing and confirmed provider reputation
Start a VPS Comparison Chart (downloadable)
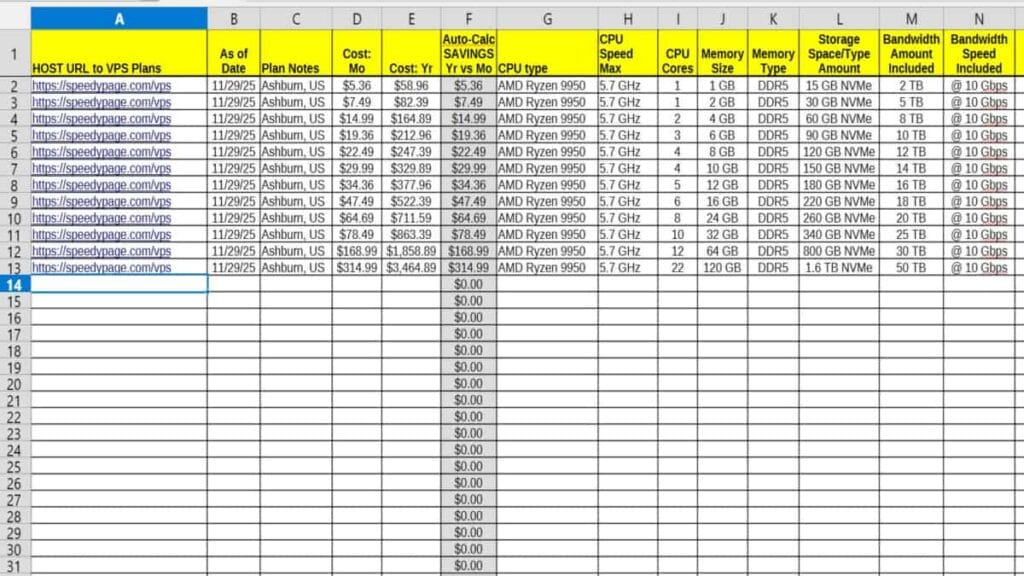
Start using your own custom server plan Comparison Chart. Downloadable VPS spreadsheet templates in 2 formats: Libre Office Calc or Microsoft Excel. Includes Speedy Page plans as a great illustrated usage example to start you off. Tap for downloads from this list:
Providers to consider (examples)
For a quick comparison of responsibilities and trade-offs, see our Managed vs Unmanaged VPS guide.
- Common providers: DigitalOcean, Linode, Vultr — widely used with mature platforms and APIs.
- Performance-focused / trusted niche hosts: SpeedyPage (user-tested fast), Hetzner (strong value/performance in Europe), OVHcloud (large network options).
- Additional reliable choices: Contabo, Scaleway, Kamatera — check support and region availability. Note: I recommend running a short trial instance and real-world tests before migrating critical services.
What to Do Next
Once you’ve picked a provider that meets these criteria, follow the Linux VPS setup checklist to get your server online with a clean, repeatable process.
Conclusion
Picking the right unmanaged VPS hosting is about matching infrastructure specs, network capacity, and tooling to your workload while ensuring backups, security, and predictable costs. Use this eight-point checklist, run short trials, and confirm restore and support workflows before moving production services there. Once you’ve picked a provider that meets these criteria, follow the How to Set Up a Linux VPS – Commands Checklist to bring your new server online with a clean, repeatable setup.
Next Steps after choosing a VPS Host Provider
This guide fits into the larger path we use on the site, so after choosing a host you can follow the roadmap laid out on the DirectAdmin VPS home page to continue with installation, DNS, and email.
Finally, don’t forget earlier shown, downloadable template and start your own custom comparison spreadsheet. Be sure to share this post!

